Breathable Films: Material Properties and Industrial Applications
Breathable films are specialized polymeric membranes engineered to allow the passage of water vapor (moisture) while acting as a barrier to liquid water, particulates, and often microorganisms. This selective permeability—commonly measured as moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR)—makes breathable films essential in applications requiring comfort, protection, and hygiene, such as personal care products, medical garments, construction materials, and packaging.
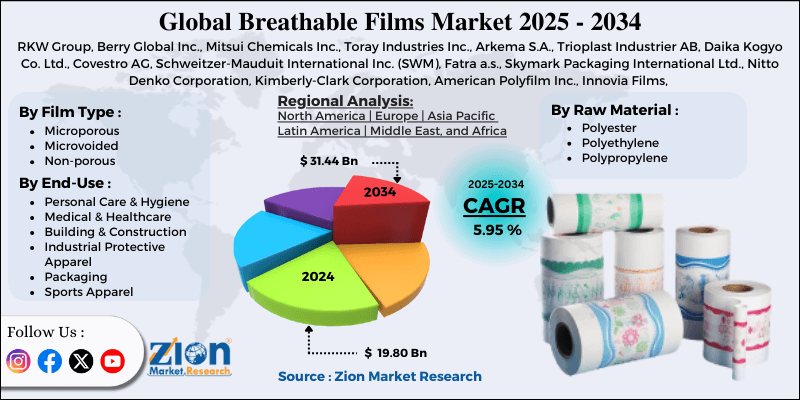
The technology traces to the 1970s-1980s with early microporous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) films (Gore-Tex, 1976) for outdoor apparel. Commercial expansion in the 1990s targeted hygiene (diapers, feminine products) and medical markets. As of 2025, the Global Breathable Films Market is valued at approximately USD 4-5 billion, growing at 7-9% CAGR driven by rising demand for premium baby diapers, adult incontinence products, surgical drapes/gowns, and sustainable building membranes. Key drivers include population aging, hygiene awareness post-COVID, and eco-friendly innovations (bio-based, recyclable films). Major producers include Berry Global, RKW Group, Mitsui Chemicals, Toray, Schweitzer-Mauduit (SWM), and Clopay (Berry), with Asia-Pacific (China, India) leading production.
Breathable films balance barrier protection with comfort, preventing moisture buildup while blocking liquids and pathogens.
Types of Breathable Films
Breathable films are classified by structure and mechanism:
- Microporous Films Dominant type (~70-80% market).
- Structure: Stretched polyethylene/polypropylene with micro-pores (0.1-5 μm).
- Mechanism: Vapor diffuses through pores; liquid blocked by surface tension.
- MVTR: 1,000-10,000 g/m²/24h.
- Uses: Diapers backsheets, medical gowns.
- Monolithic (Non-Porous) Films Hydrophilic polyurethane or copolyester.
- Mechanism: Molecular diffusion/absorption of water vapor.
- MVTR: 500-5,000 g/m²/24h.
- Advantages: Virus-proof, softer feel.
- Uses: Premium medical, wound dressings.
- Hybrid/Multilayer Films Combine microporous + monolithic layers for optimized barrier/MVTR.
- Bio-Based/Biodegradable PLA, PHA, or starch-based; emerging for sustainability.
- Specialty
- Antimicrobial-infused.
- High-barrier (virus-proof for surgical).
- Elastic (stretchable diapers).
Manufacturing Processes
- Cast Film Extrusion Melted polymer extruded onto chill roll; common for monolithic.
- Blown Film Extrusion Bubble method; multi-layer capability.
- Stretching/Orientation Key for microporous: Machine direction (MDO) or biaxial stretching creates pores.
- Lamination Breathable film bonded to nonwovens (spunbond) for hygiene/medical laminates.
- Coating Monolithic layers applied to substrates.
Sustainability: Recycled resins, solvent-free processes.
Properties and Performance
Key metrics:
- MVTR: 1,000-15,000+ g/m²/24h (ASTM E96).
- Hydrostatic Head: Liquid barrier (>1,000 mm water column).
- Air Permeability: Low for barrier applications.
- Softness/Noise: Critical for diapers (quiet films).
- Virus Barrier: EN 14126 for medical.
Advantages:
- Comfort (no sweat buildup).
- Hygiene (blocks bacteria/viruses).
- Lightweight.
Applications
- Personal Hygiene (50-60% market)
- Baby diapers/adult incontinence backsheets.
- Feminine hygiene.
- Medical and Protective Apparel
- Surgical gowns/drapes.
- Wound dressings.
- Construction
- Housewrap/roofing underlayment (vapor-permeable, liquid barrier).
- Packaging
- Fresh produce (controlled atmosphere).
- Industrial
- Filtration media, protective covers.
Market Trends
- Premium hygiene (softer, thinner).
- Sustainable (bio-PE, recycled).
- High-barrier medical (post-pandemic).
- Asia-Pacific growth (population, manufacturing).
- Smart films (moisture-sensing).
Challenges
- Cost vs. non-breathable.
- Recycling (multi-layer).
- Performance balance (high MVTR vs. barrier).
Environmental Impact
- Positive: Reduced diaper bulk, extended produce shelf life.
- Concerns: Plastic waste; shift to biodegradable.
Conclusion
Breathable films enable comfort and protection in hygiene, medical, and construction applications through selective vapor permeability. Microporous and monolithic technologies meet diverse needs, with ongoing innovation addressing sustainability and performance. As consumer expectations for eco-friendly, high-function products rise, breathable films remain vital in balancing barrier properties with breathability for health, comfort, and environmental goals.
More articles by ZMR Researche:
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/interconnect-data-center-solution-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/resolvers-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/escape-room-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/rx-medical-food-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/immunochemistry-analyzers-market